MusicStore - Part3 - EF to SQL Server
02 Mar 2019In MusicStore - Part1 - Init, in memory resources and test users had been used for test purpose.
// Startup.cs in IdentityServer
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
......
services.AddIdentityServer()
.AddDeveloperSigningCredential()
.AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Resources.GetIdentityResources())
.AddInMemoryApiResources(Resources.GetApiResources())
.AddInMemoryClients(new PortalClientFactory(Configuration).GetClients())
.AddTestUsers(TestUsers.Users);
......
}
In real world, credentials always be stored in database. Thus, I will use SQL Server + Entity Framework to replace in memory resources.
-
Create a new database called MusicStore_IdentityServer
// appsettings.Development.json "ConnectionStrings": { "IdentityServer4Connection": "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=MusicStore_IdentityServer;Integrated Security=False;User ID=musicstore_user;Password=P@ssword!@#$;" } -
Migrate resources to SQL Server
- Run CMD and navigate to Projects > IdentityServer folder
-
Use EF Code First to migrate PersistedGrantDb schema to C# script
dotnet ef migrations add InitialIdentityServerPersistedGrantDbMigration -c PersistedGrantDbContext -o Migrations/IdentityServer/PersistedGrantDb -
Use EF Code First to migrate ConfigurationDb schema to C# script
dotnet ef migrations add InitialIdentityServerConfigurationDbMigration -c ConfigurationDbContext -o Migrations/IdentityServer/ConfigurationDb - Import EF scripts to database in IdentityServer start-up
// Startup.cs public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) { // Init Database using EF Code First InitializeDatabase(app); app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseIdentityServer(); app.UseMvcWithDefaultRoute(); } private void InitializeDatabase(IApplicationBuilder app) { using (var serviceScope = app.ApplicationServices.GetService<IServiceScopeFactory>().CreateScope()) { //PersistedGrant DB Context var persistedGrantContext = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<PersistedGrantDbContext>(); persistedGrantContext.Database.Migrate(); //Configuration DB Context var configContext = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ConfigurationDbContext>(); configContext.Database.Migrate(); if (!configContext.Clients.Any()) { var clientList = new PortalClientFactory(Configuration).GetClients(); if (clientList != null && clientList.Any()) { foreach (var client in clientList) { configContext.Clients.Add(client.ToEntity()); } configContext.SaveChanges(); } } if (!configContext.IdentityResources.Any()) { foreach (var resource in Resources.GetIdentityResources()) { configContext.IdentityResources.Add(resource.ToEntity()); } configContext.SaveChanges(); } if (!configContext.ApiResources.Any()) { foreach (var resource in Resources.GetApiResources()) { configContext.ApiResources.Add(resource.ToEntity()); } configContext.SaveChanges(); } } } - Run IdentityServer project
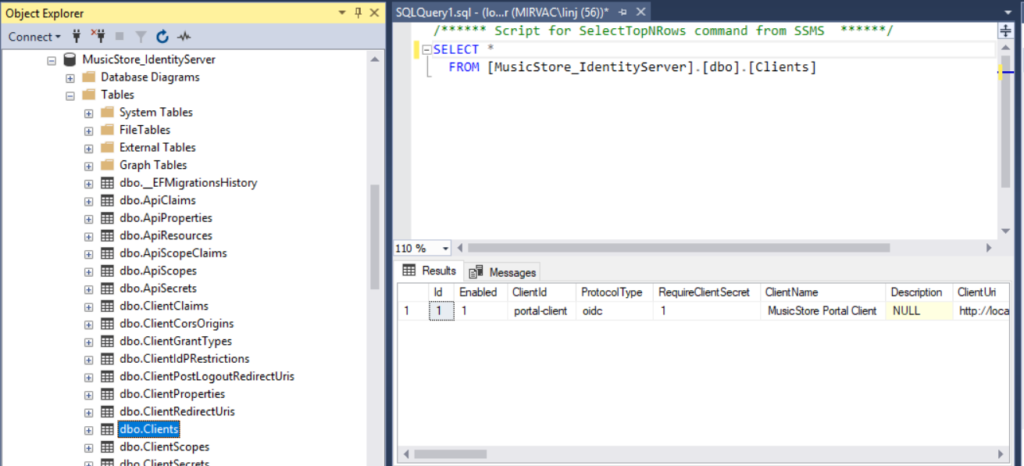
- Check if database tables are auto generated
-
Check if clients are imported correctly
- Integrate ASP.NET Identity
- Create a new .NET Standard project under Core folder called Domain
- Create a new class “ApplicationUser” to inherit from IdentityUser
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public DateTime DOB { get; set; } public int Gender { get; set; } public string Avatar { get; set; } public int Language { get; set; } public bool Enabled { get; set; } public EnumUserType UserType { get; set; } } - Create a new .NET Standard project under Foundations folder called SQLServer
-
Create a new class “AspNetIdentityDbContext” to inherit from IdentityDbContext
public class AspNetIdentityDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser> { ...... } - Run CMD and navigate to Foundations > SQLServer
-
Use EF Code First to migrate AspNetIdentityDbContext schema to C# script
dotnet ef migrations add InitialAspNetIdentityDbMigration -c AspNetIdentityDbContext -o Migrations/AspNetIdentityDb -s ../../Projects/IdentityServer -
Import EF scripts for AspNet Identity
Append this code snip to InitializeDatabase method
// AspNet Identity DB Context var idContext = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<AspNetIdentityDbContext>(); if (!idContext.Users.Any()) { var userManager = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetService<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>(); foreach (var user in Resources.GetApplicationUsers()) { var result1 = userManager.CreateAsync(user , "Test123!").Result; } } idContext.Database.Migrate(); - Run IdentityServer project
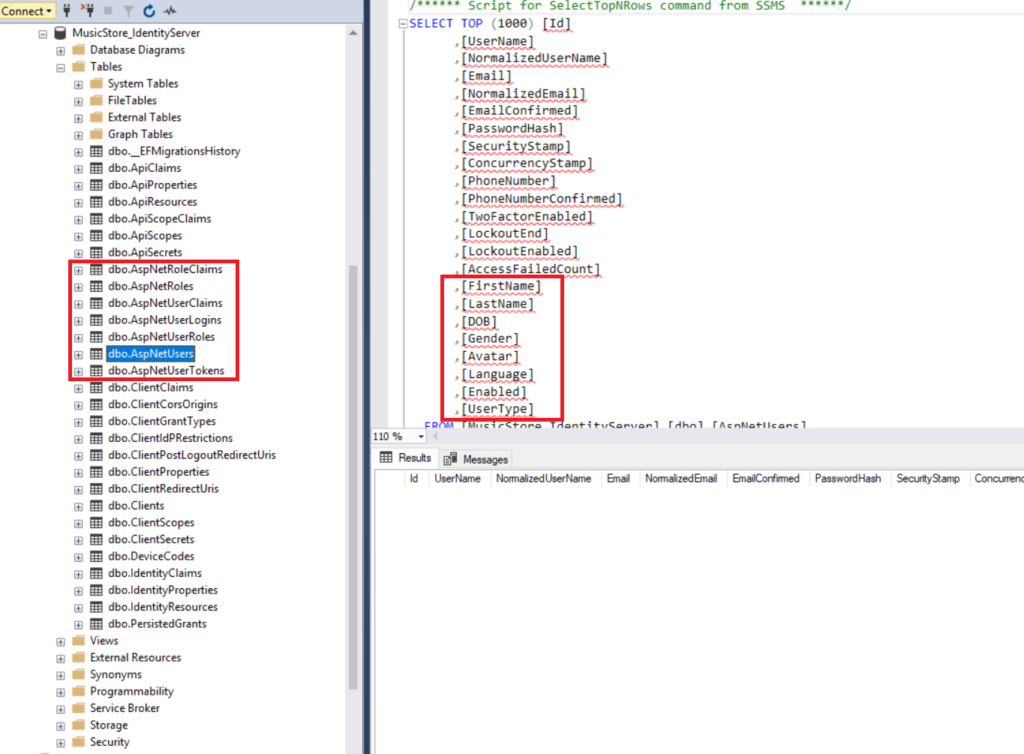
-
Check if database tables and fields are auto generated
-
Replace in memory resources
-
Init DbContext ConnectionString
//Startup.cs public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { ...... var connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("IdentityServer4Connection"); // Init DbContext ConnectionString var aspnetIdentityAssembly = typeof(AspNetIdentityDbContext).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.GetName().Name; services.AddDbContext<AspNetIdentityDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(aspnetIdentityAssembly)) ); ...... } -
Authenticate via AspNet Identity
//Startup.cs public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { ...... // Apply AspNetIdentity as default token provider // UserManager can be used to manage users services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>(options => { // Password settings options.Password.RequireDigit = true; options.Password.RequiredLength = 8; options.Password.RequireLowercase = true; options.Password.RequireNonAlphanumeric = true; options.Password.RequireUppercase = true; // User settings options.User.RequireUniqueEmail = true; }) .AddEntityFrameworkStores<AspNetIdentityDbContext>() .AddDefaultTokenProviders(); } -
Load resources from SQL Server
//Startup.cs public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { ...... // Load resources from DB var identityServerAssembly = typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.GetName().Name; var identityServer = services .AddIdentityServer() .AddAspNetIdentity<ApplicationUser>() // this adds the config data from DB (clients, resources, CORS) .AddConfigurationStore(options => { options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(identityServerAssembly)); }) // this adds the operational data from DB (codes, tokens, consents) .AddOperationalStore(options => { options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(identityServerAssembly)); // this enables automatic token cleanup. this is optional. options.EnableTokenCleanup = true; // options.TokenCleanupInterval = 15; // interval in seconds. 15 seconds useful for debugging }); ...... }services.AddDbContext<AspNetIdentityDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(aspnetIdentityAssembly)) );
-
-
Test
Use either bob / Test123$ or alice / Test123$ to login, new password “Test123$” has been applied because of the password settings in #4



